Identity
Definition Of Identity
Identity Equation: An equation which is true for every value of the variable is called an identity equation.
Examples of identity equation: 5(a - 3) = 5a - 15, (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
Identity Inequality: An inequality which is true for every value of the variable is called an identity inequality.
For example, the inequality a2 ≥ 0 is true for every value of a.
Identity Function: A function in which the domain values doesn't change at all. f (x) = x is an identity function.
Identity Matrix: Its a square matrix with 1 for each element on the main diagonal and 0
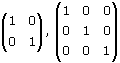
for all other elements are identity matrices of dimension 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 respectively. The product of n × n matrix and the identity matrix gives back the n × n matrix.
Video Examples: Algebraic expressions and identities
Solved Example on Identity
Ques: Solve the equation 5(x + 2) = 5x + 10 and determine whether it has one solution, no solution, or is an identity.
Choices:
A. an identity
B. one solution
C. not enough information given
D. no solution
Correct Answer: A
Solution:
Step 1: 5(x + 2) = 5x + 10 [Given equation.]
Step 2: 5x + 10 = 5x + 10 [Multiply 5 to remove the parenthesis.]
Step 3: 5x + 10 - 5x = 5x + 10 - 5x [Subtract 5x from each side.]
Step 4: 10 = 10 [Combine like terms.]
Step 5: 10 = 10 is always true. So, the given equation is an identity.